OSE Piping Workbench Ports: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Ruslan (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Ruslan (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 43: | Zeile 43: | ||
* <math>A'^{-1}</math> rotates the fitting in such a way that its port points to x-direction, and 0 reference to y-direction. | * <math>A'^{-1}</math> rotates the fitting in such a way that its port points to x-direction, and 0 reference to y-direction. | ||
* <math>A_r</math> rotates the fitting opposite to x-direction, but its 0 reference still points to y-direction. | * <math>A_r</math> rotates the fitting opposite to x-direction, but its 0 reference still points to y-direction. | ||
| − | * <math>A</math> gives to the rotated fitting the same orientation as the port of the other fitting. | + | * <math>R\cdot A</math> gives to the rotated fitting the same orientation as the port of the other fitting in glbal coordinates. |
| − | We have <math display="block">B:=A'^{-1}\cdot A_r \cdot A</math>. | + | We have <math display="block">B:=A'^{-1}\cdot A_r \cdot R\cdot A</math>. |
== Ports in Python == | == Ports in Python == | ||
In ''OsePiping.Port'' class the port position and orientation are stored in the ''Port.placement'' attribute as a ''FreeCAD.Placement'' object. | In ''OsePiping.Port'' class the port position and orientation are stored in the ''Port.placement'' attribute as a ''FreeCAD.Placement'' object. | ||
Version vom 1. Dezember 2018, 18:37 Uhr
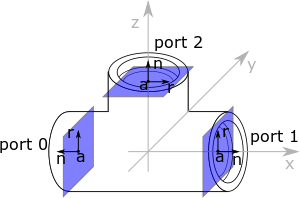
Ports
The OSE Piping Workbench creates fittings. It uses ports to describe the ends of the fittings. The Ports helps to fit the fittings together correctly.
Every port is described by:
- Its position .
- A normal vector which points out of the fitting and it is perpendicular to the port plane.
- A 0 reference angle vector it shows where is the degree 0°. must lie in the port plane.
All three vectors refer to local coordinates.
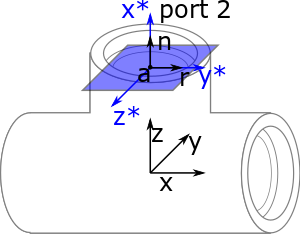
Instead of using three separate vectors, we represent the port by its position and its orientation .
The position is a FreeCAD Vector . The orientation is a FreeCAD rotation matrix. When we apply matrix on vectors , , , it creates vectors , , such that
- points in the same direction as the port's normal, .
- shows in the same direction as the angular reference, .
For example in a tee fitting, the matrix is a rotation along y-axis by , and then a rotation along z axis by . See FreeCAD Rotation for more details about rotation.
Adjust two fittings
When we adjust one fitting to another we want rotate the first fitting in such a way that its socket points in opposite directions as a socket of the other fitting. Let us assume that the port of the adjusting fitting has position , orientation with normal and 0 degree reference . Everything refering to the local coordinates of the fitting.
The other fitting has position and rotation . The local properties of its port has has local position , local orientation , local normal and local 0 degree reference . That means the corresponding global parameter of the port are
We want to find a rotation matrix , such that applying it to adjusting fitting the new orientation of its port *in relating to global coordinate* has following properties:
- Its normal vector looks to opposite direction as the normal of the other fitting: .
- Its zero-degree reference points to the same direction
We compose the matrix from three matrices Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle A_r} and Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle A} .
- Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle A'^{-1}} rotates the fitting in such a way that its port points to x-direction, and 0 reference to y-direction.
- Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle A_r} rotates the fitting opposite to x-direction, but its 0 reference still points to y-direction.
- Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle R\cdot A} gives to the rotated fitting the same orientation as the port of the other fitting in glbal coordinates.
We have Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle B:=A'^{-1}\cdot A_r \cdot R\cdot A} .
Ports in Python
In OsePiping.Port class the port position and orientation are stored in the Port.placement attribute as a FreeCAD.Placement object.